America's Illegal Immigration Predicament

PORTLAND, USA, May 03 (IPS) - Approximately 225 million people from around the world would like to migrate permanently to the United States. But given America’s current policies, relatively few of them will be able to do so legally.
In 2021 the number of persons who obtained lawful resident status in the United States was 740 thousand. Also, based on past trends, population projections of the U.S. Census Bureau for the coming four decades estimate an annual addition of approximately 1.1 million legal immigrants to America’s population.
Consequently, millions of men, women and children wanting to emigrate to America but unable to do so legally are resorting to illegal immigration. In 2021, an estimated 1.13 million people unlawfully migrated to America and during fiscal year 2022 more than 1.6 million migrants were apprehended illegally crossing the border.
In addition, many illegal migrants are willing to risk their personal safety and lives to reach America. During the past twelve months, no less than 853 migrants died trying to reach America from Mexico, making fiscal year 2022 the deadliest year for unauthorized migrants recorded by the U.S. government.
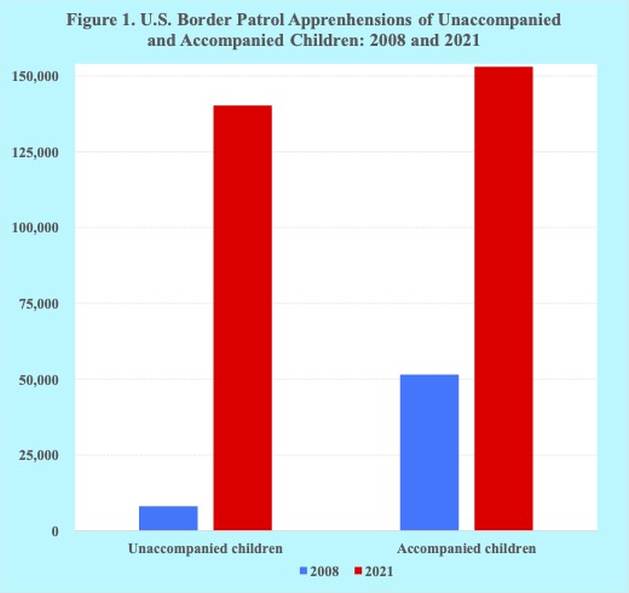
Furthermore, over the past fifteen years the number of children encountered by Border Patrol officers at the southern border has grown enormously. Since fiscal year 2008, the number of apprehensions of unaccompanied children has increased seventeen-fold, reaching a total of nearly 622 thousand.
Approximately 97 percent of the unaccompanied children come from four countries: Guatemala (32 percent), Honduras (28 percent), Mexico (21 percent) and El Salvador (16 percent). Also, between 2008 and 2019, the number of both unaccompanied and accompanied children apprehended at the southern border, reaching an overall total of 1.35 million, has risen five-fold (Figure 1).
On May 11, the administration is expected to end the Title 42 COVID-19 pandemic policy. That policy, which was relied on extensively by the previous administration, allowed officials to turn away hundreds of thousands of people without offering them an opportunity to claim asylum.
Also, earlier in March, another administration policy, referred to as Parole plus Alternative to Detention, was stopped by a Florida court. That policy aimed at reducing unauthorized migration pressures through the use of ankle monitors or a phone app.
Despite the announcements and assurances by senior officials in the Biden administration, including Secretary State Antony J. Blinken and Homeland Security Secretary Alejandro N. Mayorkas, to limit the flow of unauthorized migrants across the U.S. southern border, the combination of the court’s March decision and the ending of Title 42 is expected to lead to a massive surge of tens of thousands more unauthorized migrants arriving at the southern border. The estimated illegal crossings could reach as high as 18,000 a day.
As has been the case in the recent past, such large numbers of unauthorized migrants are already overwhelming border resources and overcrowd government facilities. By the end of April more than 20,000 migrants were in Border Patrol custody, which is more than twice the rated capacity of the agency’s detention facilities along the U.S. southern border.
Those developments are expected to be followed by the release of many unauthorized migrants into the country without a court date, which is widely viewed as an incentive to additional illegal entries. That decision in turn will continue to incur costs and create pressures on border communities as well as cities in the country’s interior.
Bracing itself for the expected surge of unauthorized migrants at the country’s southern border, the Biden administration is implementing various immigration measures to address the illegal immigration crisis.
Among those measures are to open regional processing centers, increase refugee numbers from the Western hemisphere, have migrants enroll in the parole programs, schedule an appointment at the border via an app, seek asylum protection in a country they traveled through and increase pathways for legal immigration, including for El Salvadorans Hondurans and Guatemalans to reunite with family in the U.S.
Although two Republican sponsored immigration bills are proceeding through the U.S. House of Representatives, Congress has yet to pass immigration legislation and is unlikely to do so with the run up to the 2024 elections. As a result, President Biden has used his executive authority for measures to open the doors for hundreds of thousands of migrants to enter America legally.
In addition to the use of humanitarian parole programs for people fleeing war and political upheaval, the Biden administration’s measures offer migrants opportunities to enter the U.S. and secure work authorization if they have a private sponsor. By mid-April, about 300 thousand Ukrainians had arrived in America and by the close of 2023, approximately 360 thousand migrants from Latin America are expected to be admitted legally via private sponsorship.
Also with some exceptions, the administration plans to bar from asylum all non-Mexican migrants who arrive at the southern U.S. border without having first sought and been denied asylum in at least one of the countries they passed through on their trip. However, rights groups and their supporters oppose that plan as they believe it violates U.S. law and have threatened to sue the administration.
The root cause for illegal immigration to the U.S. is not complicated. Most unauthorized migrants coming to America are doing so to escape difficult living conditions. The administration’s foreign aid initiative to improve living conditions in countries such as El Salvador, Guatemala and Honduras has done relatively little to stem the historic levels of illegal immigration at the southern border.
It is certainly understandable that many of those living under harsh conditions, including poverty, unemployment, lack of basic services, violence and political instability, want to emigrate. However, such living conditions are generally not grounds to permit legal entry into America.
Consequently, many of the unauthorized migrants arriving at the U.S. southern border are claiming asylum. To date, nearly 1.6 million asylum applications are pending in U.S. Citizenship and Immigration services and immigration courts, which is the largest number of pending cases on record.
According to Article 14 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, everyone has the right to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution. Asylum is granted to persons who can demonstrate that they are unable or unwilling to return to their country because of persecution or a well-founded fear of persecution on account of race, religion, nationality, political opinion or membership in a particular group.
Most of the migrants who have claimed asylum in the U.S. are not detained. In 2022, approximately 80 percent of the unauthorized migrants in the immigration court asylum backlog were never detained.
Those migrants were permitted to remain in the country while their cases are processed, which take on average more than four years. During that period of time, migrants take steps to integrate themselves into local communities, especially places offering sanctuary to illegal migrants.
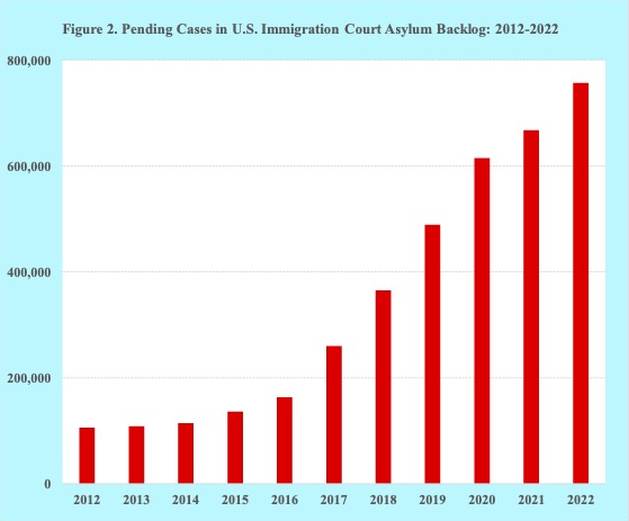
The number of pending cases in the U.S. immigration court asylum backlog has grown rapidly over the recent past. Between 2012 and 2022 the number of pending cases in the asylum backlog increased seven-fold, i.e., from about 106 thousand to 757 thousand (Figure 2).
Most claims for asylum in the U.S. fail to meet the criteria needed to be granted asylum. Over the past several years, approximately 70 percent of the asylum claims have been denied.
Nevertheless, relatively few of the migrants whose claims have been denied are repatriated. The number of non-citizen removals conducted by U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement in fiscal year 2022 is 72,117.
With a growing world population of 8 billion, the supply of people who want to migrate to the U.S., estimated at approximately 225 million people, greatly exceeds America’s demand for migrants, which is a small fraction of the worldwide supply.
Consequently, as a result of the substantial demographic and economic imbalances, millions of men, women and children are resorting to illegal migration to secure a better life in America. As of yet, neither Congress nor the White House have come up with an effective blueprint to address America’s illegal immigration predicament.
Joseph Chamie is a consulting demographer, a former director of the United Nations Population Division and author of numerous publications on population issues, including his recent book, "Population Levels, Trends and Differentials: More Important Population Matters”.
© Inter Press Service (2023) — All Rights Reserved. Original source: Inter Press Service

